 |
ros2_control - rolling
|
 |
ros2_control - rolling
|
Classes | |
| class | ActuatorHandle |
| class | DifferentialTransmission |
| class | DifferentialTransmissionLoader |
| Class for loading a four-bar linkage transmission instance from configuration data. More... | |
| class | Exception |
| class | FourBarLinkageTransmission |
| Implementation of a four-bar-linkage transmission. More... | |
| class | FourBarLinkageTransmissionLoader |
| Class for loading a four-bar linkage transmission instance from configuration data. More... | |
| class | Handle |
| class | JointHandle |
| class | SimpleTransmission |
| class | SimpleTransmissionLoader |
| Class for loading a simple transmission instance from configuration data. More... | |
| class | Transmission |
| Abstract base class for representing mechanical transmissions. More... | |
| class | TransmissionInterfaceException |
| class | TransmissionLoader |
| Abstract interface for loading transmission instances from configuration data. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef std::shared_ptr< Transmission > | TransmissionSharedPtr |
Variables | |
| constexpr auto | HW_IF_ABSOLUTE_POSITION = "absolute_position" |
| Implementation of a differential transmission. | |
|
constexpr |
Implementation of a differential transmission.
Implementation of a simple reducer transmission.
This transmission relates two actuators and two joints through a differential mechanism, as illustrated below.
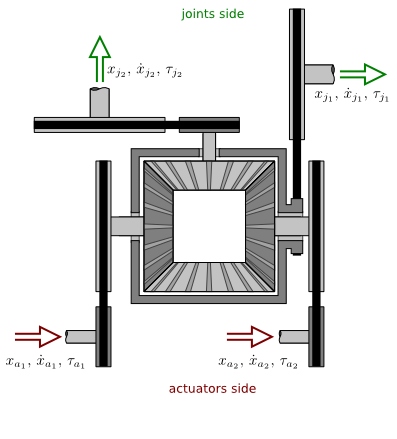
| Actuator to joint | \begin{eqnarray*} \tau_{j_1} & = & n_{j_1} ( n_{a_1} \tau_{a_1} + n_{a_2} \tau_{a_2} ) \\[2.5em] \tau_{j_2} & = & n_{j_2} ( n_{a_1} \tau_{a_1} + n_{a_2} \tau_{a_2} ) \end{eqnarray*} | \begin{eqnarray*} \dot{x}_{j_1} & = & \frac{ \dot{x}_{a_1} / n_{a_1} + \dot{x}_{a_2} / n_{a_2} }{2 n_{j_1}} \\[1em] \dot{x}_{j_2} & = & \frac{ \dot{x}_{a_1} / n_{a_1} - \dot{x}_{a_2} / n_{a_2} }{2 n_{j_2}} \end{eqnarray*} | \begin{eqnarray*} x_{j_1} & = & \frac{ x_{a_1} / n_{a_1} + x_{a_2} / n_{a_2} }{2 n_{j_1}} + x_{off_1} \\[1em] x_{j_2} & = & \frac{ x_{a_1} / n_{a_1} - x_{a_2} / n_{a_2} }{2 n_{j_1}} + x_{off_2} \end{eqnarray*} |
| Joint to actuator | \begin{eqnarray*} \tau_{a_1} & = & \frac{ \tau_{j_1} / n_{j_1} + \tau_{j_2} / n_{j_2} }{2 n_{a_1}} \\[1em] \tau_{a_2} & = & \frac{ \tau_{j_1} / n_{j_1} - \tau_{j_2} / n_{j_2} }{2 n_{a_1}} \end{eqnarray*} | \begin{eqnarray*} \dot{x}_{a_1} & = & n_{a_1} ( n_{j_1} \dot{x}_{j_1} + n_{j_2} \dot{x}_{j_2} ) \\[2.5em] \dot{x}_{a_2} & = & n_{a_2} ( n_{j_1} \dot{x}_{j_1} - n_{j_2} \dot{x}_{j_2} ) \end{eqnarray*} | \begin{eqnarray*} x_{a_1} & = & n_{a_1} \left[ n_{j_1} (x_{j_1} - x_{off_1}) + n_{j_2} (x_{j_2} - x_{off_2}) \right] \\[2.5em] x_{a_2} & = & n_{a_2} \left[ n_{j_1} (x_{j_1} - x_{off_1}) - n_{j_2} (x_{j_2} - x_{off_2}) \right] \end{eqnarray*} |
where:
This transmission relates one actuator and one joint through a reductor (or amplifier). Timing belts and gears are examples of this transmission type, and are illustrated below.
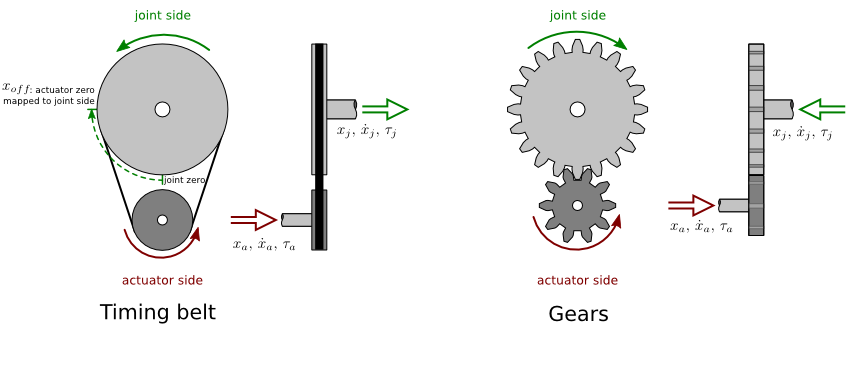
| Actuator to joint | \[ \tau_j = n \tau_a \] | \[ \dot{x}_j = \dot{x}_a / n \] | \[ x_j = x_a / n + x_{off} \] |
| Joint to actuator | \[ \tau_a = \tau_j / n\] | \[ \dot{x}_a = n \dot{x}_j \] | \[ x_a = n (x_j - x_{off}) \] |
where: