 |
ros2_control - humble
|
 |
ros2_control - humble
|
Virtual Class to implement when integrating a stand-alone sensor into ros2_control. More...
#include <sensor_interface.hpp>

Public Member Functions | |
| SensorInterface (const SensorInterface &other)=delete | |
| SensorInterface copy constructor is actively deleted. | |
| SensorInterface (SensorInterface &&other)=default | |
| virtual CallbackReturn | on_init (const HardwareInfo &hardware_info) |
| Initialization of the hardware interface from data parsed from the robot's URDF. | |
| virtual std::vector< StateInterface > | export_state_interfaces ()=0 |
| Exports all state interfaces for this hardware interface. | |
| virtual return_type | read (const rclcpp::Time &time, const rclcpp::Duration &period)=0 |
| Read the current state values from the actuator. | |
| virtual std::string | get_name () const |
| Get name of the actuator hardware. | |
| const rclcpp_lifecycle::State & | get_state () const |
| Get life-cycle state of the actuator hardware. | |
| void | set_state (const rclcpp_lifecycle::State &new_state) |
| Set life-cycle state of the actuator hardware. | |
Protected Attributes | |
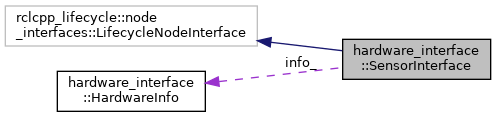
| HardwareInfo | info_ |
| rclcpp_lifecycle::State | lifecycle_state_ |
Virtual Class to implement when integrating a stand-alone sensor into ros2_control.
The typical examples are Force-Torque Sensor (FTS), Interial Measurement Unit (IMU).
Methods return values have type rclcpp_lifecycle::node_interfaces::LifecycleNodeInterface::CallbackReturn with the following meaning:
The hardware ends after each method in a state with the following meaning:
UNCONFIGURED (on_init, on_cleanup): Hardware is initialized but communication is not started and therefore no interface is available.
INACTIVE (on_configure, on_deactivate): Communication with the hardware is started and it is configured. States can be read.
FINALIZED (on_shutdown): Hardware interface is ready for unloading/destruction. Allocated memory is cleaned up.
ACTIVE (on_activate): States can be read.
|
delete |
SensorInterface copy constructor is actively deleted.
Hardware interfaces are having a unique ownership and thus can't be copied in order to avoid failed or simultaneous access to hardware.
|
pure virtual |
Exports all state interfaces for this hardware interface.
The state interfaces have to be created and transferred according to the hardware info passed in for the configuration.
Note the ownership over the state interfaces is transferred to the caller.
Implemented in ros2_control_demo_example_14::RRBotSensorPositionFeedback, and ros2_control_demo_example_5::ExternalRRBotForceTorqueSensorHardware.
|
inlinevirtual |
Get name of the actuator hardware.
|
inline |
Get life-cycle state of the actuator hardware.
|
inlinevirtual |
Initialization of the hardware interface from data parsed from the robot's URDF.
| [in] | hardware_info | structure with data from URDF. |
Reimplemented in ros2_control_demo_example_14::RRBotSensorPositionFeedback, and ros2_control_demo_example_5::ExternalRRBotForceTorqueSensorHardware.
|
pure virtual |
Read the current state values from the actuator.
The data readings from the physical hardware has to be updated and reflected accordingly in the exported state interfaces. That is, the data pointed by the interfaces shall be updated.
| [in] | time | The time at the start of this control loop iteration |
| [in] | period | The measured time taken by the last control loop iteration |
Implemented in ros2_control_demo_example_14::RRBotSensorPositionFeedback, and ros2_control_demo_example_5::ExternalRRBotForceTorqueSensorHardware.
|
inline |
Set life-cycle state of the actuator hardware.